Which Best Describes an Hypertonic Solution
Safety of Continuous Peripheral Infusion of 3 Sodium Chloride Solution in Neurocritical Care Patients. An increase in total body sodium increases the.

Hypertonic Solution Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
Mannitol a carbohydrate is supplied as a 25 wv solution.
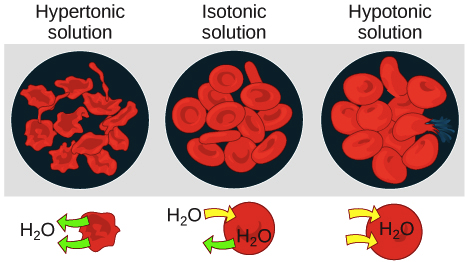
. A hypertonic solution is one that has a higher solute concentration outside the cell than inside. Hypertonic Solution Definition. A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap.
Because the cell has a lower concentration of solutes the water will leave the cell. Base Pair Nucleotides with double strand of DNA. This hypertonic solution is given to patients who have sustained a head injury with associated brain swelling.
A solution with a greater concentration of solutes lower concentration of water than the cell is referred to as a hypertonic solution A cell put in this solution will lose water and diminish which might cause cell death A solution that has the exact same concentration of solutes exact same concentration of water as the cell is an is otonic solution When. If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution the cell will shrink due to water osmotically moving out. The Starling equation describes the forces that regulate the production of interstitial fluid.
This may cause an animal cell to shrivel or. Hypertonic dehydration occurs when there is a water loss more than sodium loss which will cause an elevation in serum sodium and osmolality. Everyones Ticket to Hollywood.
In premature infants and neonates the 84 solution should be diluted 11 with 5 dextrose. If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution the cell is considered. C Water will move out of the cell.
16mmol Mg 2 IV usually in 20 solution over 5min minimum preferably 10-15 min is followed immediately by 5g MgSO 4 approx. Safety of Peripheral Line Administration of 3 Hypertonic Saline and Mannitol in the Emergency Department. B The cell will undergo osmotic lysis.
An increase in total body sodium increases plasma hydrostatic pressure due to an increase in plasma volume. Jones GM Bode L Riha H Erdman MJ. A loading dose of 4g MgSO 4 approx.
Hypotonic dehydration is most often caused by diuretics which cause sodium loss more than. In the situation of increased total body sodium. Presentation on the label must.
As the wound dries cell migration and proliferation are impeded20. Water moves out of the cell lower water concentration. Am J Crit Care 2016.
D Water will move into the cell. Whats buzzing in the hills of Hollywood. Isotonic Ringers solution homeostatic dressing from application to removal promoting moist wound healing throughout.
20mmol Mg 2 IM every. The outside solution has higher soluble concentration than inside the cell. Researchers at the University of São Paulo USP in Brazil have shown that a hypertonic saline solution inhibits replication of SARS-CoV-2 the virus that causes COVID-19 and have elucidated the.
J Emerg Med 2019. Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a bacterial cell is placed in a solution containing 5 NaCl. Mesghali E Fitter S Bahjri K Moussavi K.
Excess pure water loss mainly occurs through the lungs kidneys and skin. Deoxygenated blood away from the. What releases sodium bicarbonate.
The name also describes a group of substances that have similar characteristics and is to be used irrespective of whether one or more of the substances in the group are present in the formulation. For intravenous administration only. Maintenance therapy is a further 5g MgSO 4 approx.
A hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution. As saline evaporates becomes hypertonic and fluid from the wound is then drawn into the dressing promoting desiccation of the tissue. The opposite solution with a lower concentration is known as the hypotonic solutionScientists must describe cell contents compared to the environment.
A statement specifying whether the solution is hypotonic hypertonic or isotonic. 43 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 61 Conditions where sodium intake is restricted eg. In effect the solute is drawing the water out of the cell.
Etiologies are fever DI and increased respiration. Why is the cell in a hypertonic solution. 20mmol Mg 2 usually in 50 solution as a deep IM injection into the upper outer quadrant of each buttock.
Thus water molecules move from inside to outside the cell. And d the osmolality of the solution. Purines adenineA guanine G pyrimidines cytosine C thymine T pulmonary circuit.
Starling pressures are altered to produce pitting edema and body effusions. In a hypertonic solution the prefix hyper refers to the extracellular fluid having a higher concentration of solutes than the cells cytoplasm the fluid contains less water than the cell does. A Sucrose will move into the cell from a higher to a lower concentration.
E No change will result the solution is isotonic. 4ph to 9ph is how many times stronger.

Vocabulary List 5 1 Hypertonic Solution A Solution That Has More Solute In It Than A Cell 2 Hypotonic Solution A Solution That Has Less Solute In Ppt Download

Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions Article Khan Academy

No comments for "Which Best Describes an Hypertonic Solution"
Post a Comment